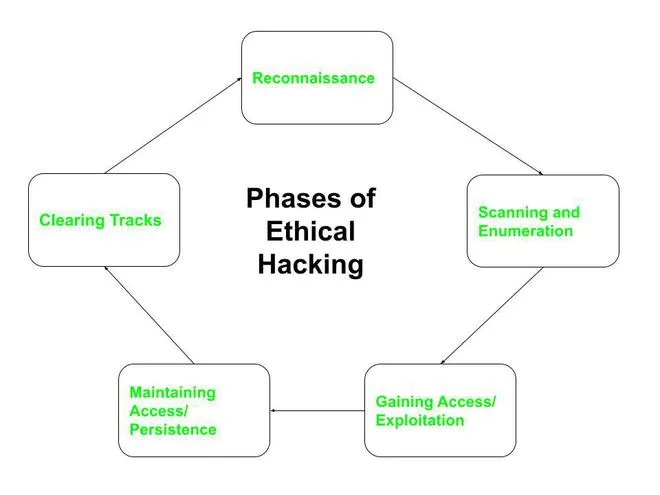
How is it that these attackers, whether they are security consultants or criminals, what do they do? Well, there are some phases of hacking and we’re going to look at the phases of ethical hack in the first phaseis Reconnaissance. In this case, what’s going to happen is the attacker, whether it be a hacker who is being paid to do it by the company or an attacker who is trying to extort money as a criminal basis, they’re going to scan, they’re going to go gather information passively by searching public records, looking at news releases, looking at LinkedIn, looking at employee information, websites, or maybe even visiting the organization and getting their trash, looking through that for paperwork or whatever.

Active is when they directly interact with the target by any means. So if you make a phone call and ask about the organization or getting an account or call employees, or use a technical and for methodologies to scan ports and equipment of the organization to find out information about it. You’re doing an active attack, you’re interacting with the organization.
The next phase after reconnaissance is scanning. In this case, we’re going to take a piece of equipment that scans, are looking at ports, pinging IP addresses, sweeping through the system, looking at vulnerabilities and vulnerability scanners.

In this case, what we’re trying to do, on the external and on the internal network is fine. Live hosts, live machines, open ports, details of operating systems and devices. We’re looking at the patch level of each of these, the version of the application, the uptime status, etc. We’re scanning or ascending and probes getting back information, finding more information about that.
After the scanning phase, the next one, if we get enough information after scanning, we want to gain access. This is where the attacker gets access to an operating system on the network and from there, they’re going to be able to look at the network at two different levels, try to escalate their privilege.

If they have a low-level user account or a guest account, they’ll want to get an account that can do more. Either they want to add privileges to their current account, or they want to take their account and get a new account, like an administrator or root account. They might do password cracking, use attacks on applications like buffer overflow attacks that can help them get into other locations to gain privilege, do denial of service, and even session hijacking to get extra privilege from a session that’s higher, has higher privilege with a host than their current capabilities. They’ll do those types of things in gaining access.
Once the attacker has gained access, the next thing you’re going to want to do is maintain access. They want to own the system. There is a term that hackers use called PWN. By the way, you can look up the history of that. It’s actually very interesting where that came up.

And so what they’re gonna do is they want to have a backdoor setup. By the time an attacker has a backdoor or a root kit, you can’t even tell it’s installed, it’s hidden out in the background. Once they have this, they can maintain access. They can get access remotely anytime they want to any system where they have a backdoor or a rootkit and they might even use a trojan to help accomplish that. They can download data, manipulate data, they’ve owned the system, and then they can use that system to launch further attacks .
Once they are maintaining access, another item, another phase is where this attacker going to clear their tracks. They’re going to hide everything they’re doing.

They’re going to stop files in places that can’t be seen. They’re gonna delete logs. They’re going to try to remain unnoticed on COD or they’re going to try to avoid suspicion. They’re going to hide their identity. They’re going to hide what they’re doing, or they may even delete five megabytes of logs and put in five megabytes of fake logs just to cover what they’re doing. Clearing the tracks is the last phase of hacking.