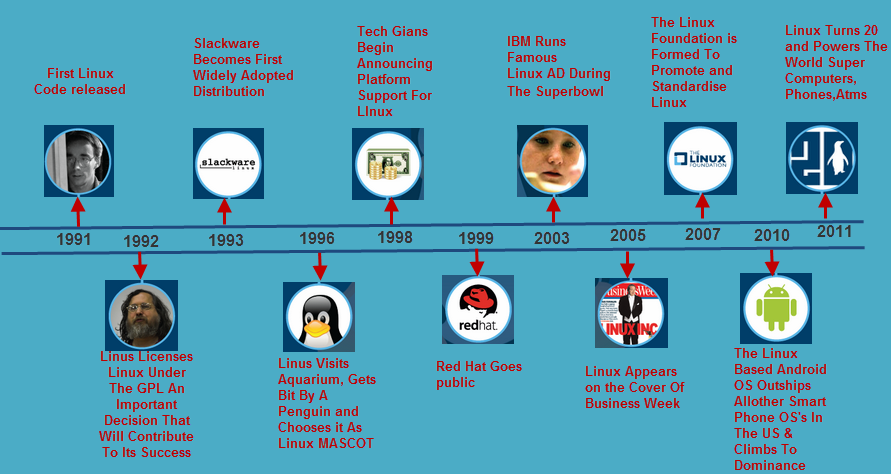
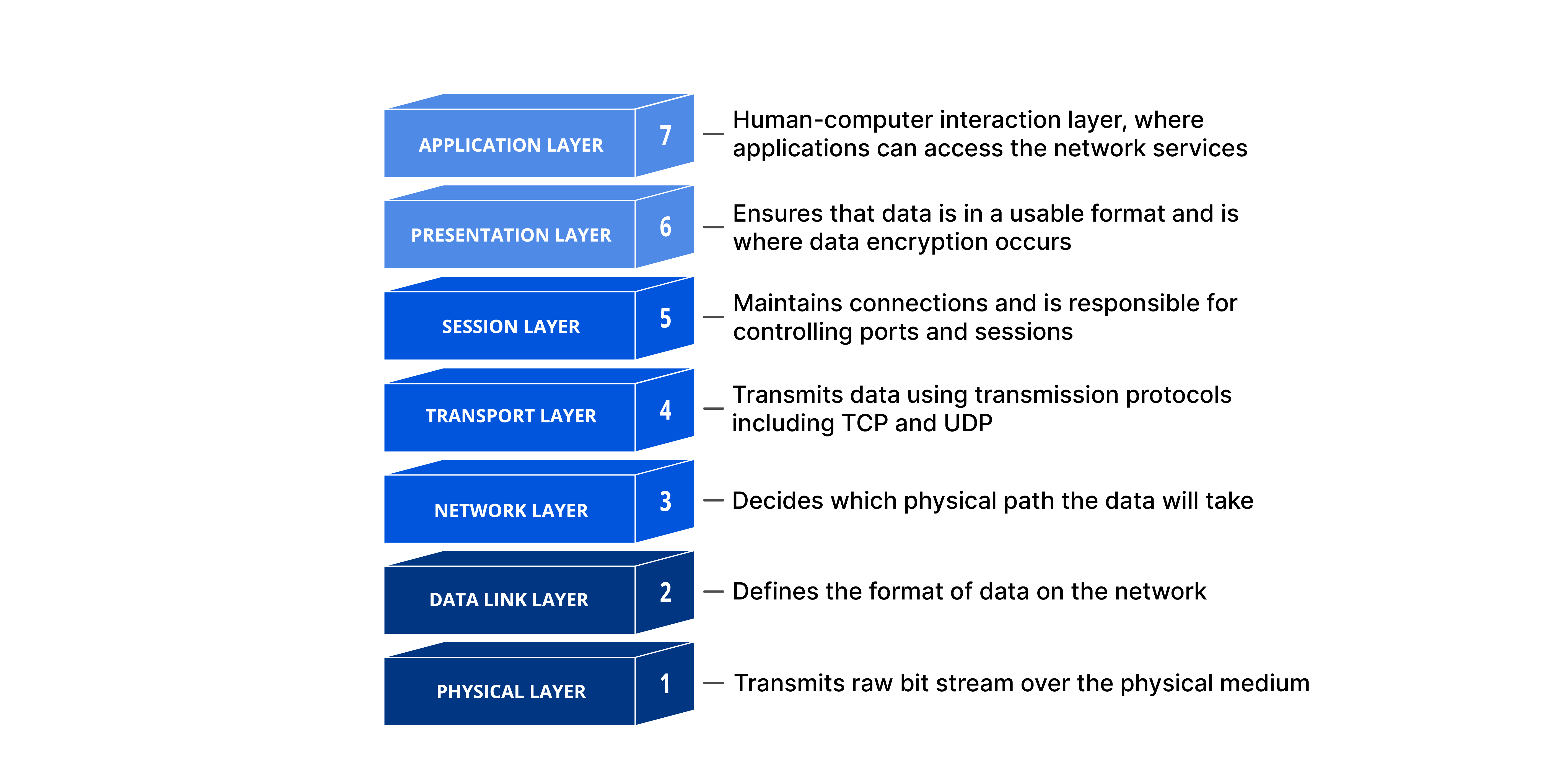
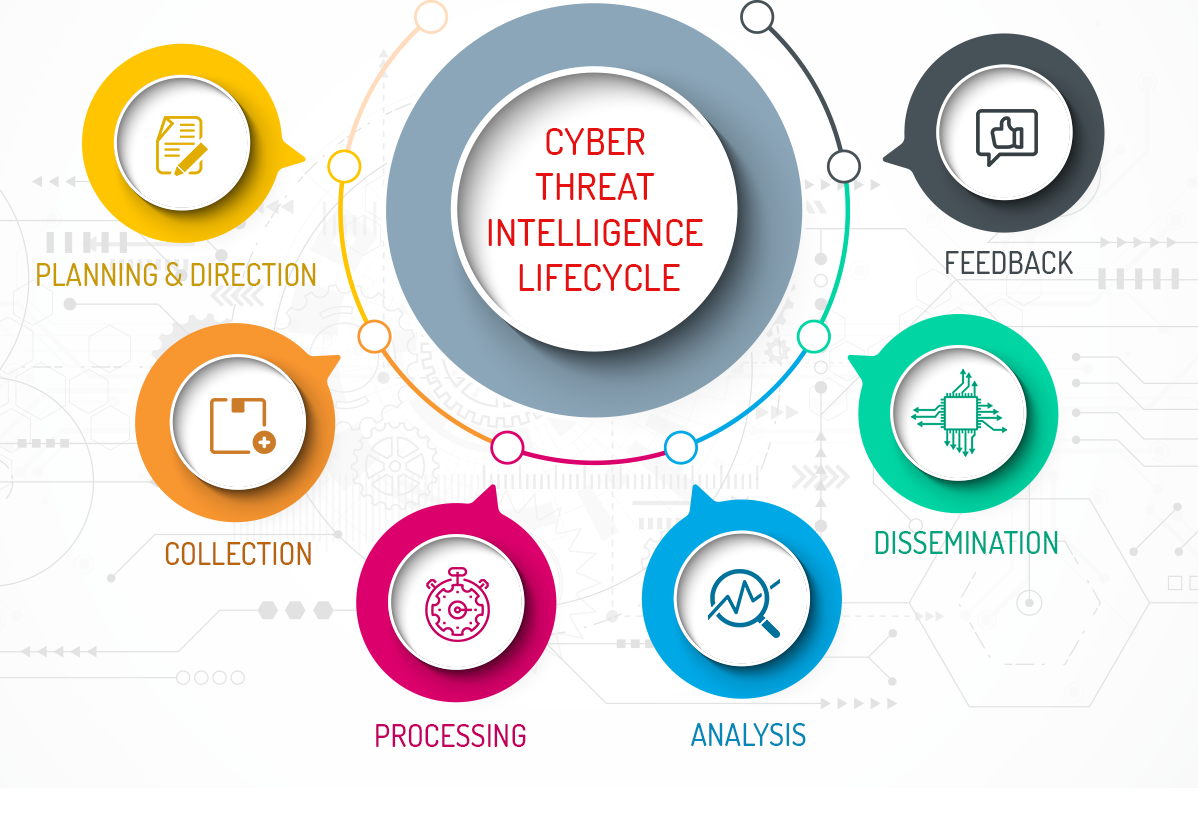
Cybersecurity
Cybersecurity refers to the practice of protecting computer systems, networks, devices, and data from unauthorized access, attacks, damage, or theft. It encompasses a wide range of technologies, processes, and practices designed to safeguard information technology assets and ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data.
Key aspects and concepts related to cybersecurity:
- Confidentiality: This principle ensures that sensitive information remains private and is only accessible by authorized individuals. Encryption, access controls, and data classification are common measures to maintain confidentiality.
- Integrity: Integrity ensures that data is accurate and unaltered. Cybersecurity measures, such as checksums and digital signatures, help detect and prevent unauthorized changes to data.
- Availability: Availability ensures that systems and data are accessible when needed. Distributed denial of service (DDoS) attacks, for example, aim to disrupt availability. Redundancy and failover mechanisms help maintain availability.
Cybersecurity is an ever-evolving field as new threats and technologies emerge. Staying vigilant and proactive in addressing cybersecurity risks is crucial for individuals, businesses, and governments to protect sensitive information and critical infrastructure.